Table of Content
With attention spans dropping like never before, smartphone users are easily distracted. Even if you ask them to visit a particular section of an app, they might soon forget to do it or may question their intentions behind installing the application in the first place.
App deep linking eliminates such inconsistencies. It can offer personalised onboarding experiences, take users to appropriate app stores to install an app, and even forward users to a specific section of an app.
It is a small trick that can significantly enhance user engagement and defines how valuable, and relevant a user finds an app to be. Let’s take a look at the technicalities behind such links and see why they are a trove for mobile app developers.
What Is App Deep Linking?
A deep link is a specialised uniform resource identifier (URI) that can open and direct a user to a specific location inside an app and not the home screen. Think of it as the app counterparts of website URLs. In fact, deep links are ubiquitous in web applications and are called direct links.
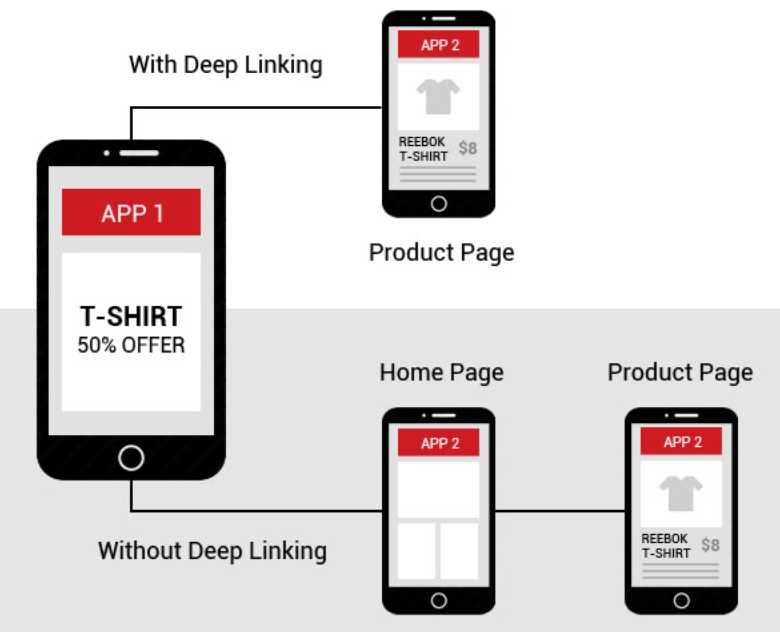 How app to app deep linking works. Image Credit: blog.contus.com
How app to app deep linking works. Image Credit: blog.contus.com
With deep linking, you are making the user journey smoother and concise by letting them reach the app goal sooner than with the usual user flow. By reducing the number of actions it takes to access the critical functions of an app, users are less likely to churn.
Without deep links, you will have to instruct users to perform specific tasks. For example, if you want a user to follow your company page on Facebook, without deep links, you will have to deliver instructions as,
- Open the Facebook app.
- Search for “”your-company-name””.
- Tap on the icon with our company logo in the search results.
- Tap on the Follow button.
With Facebook app deep linking, users can directly skip to the 4th step – leaving no room for confusion.
Deep links help in enhancing the user experience (UX) of an app by sending users directly to specific in-app locations. To put that in perspective, assume you were watching the famous Netflix series, House of Cards.
You were halfway through an episode and stopped watching it for some or the other reason. As part of their retention marketing strategy, they send you a deep link, which, when tapped, opens the app and points you to the very second of the episode you left off.
More precisely, deep links can be used to send users directly to app content from,
- Websites
- Search results
- Other apps
- Social media
- App install ads
- Emails
- SMS
If a user discovers your app from Google search results, deep linking to app stores eliminates the need for them to search for your app manually. If you manage multiple mobile applications, you can implement app to app deep linking for cross-promotion.
What Is Deep Linking in iOS?
Along with iOS 9.0, Apple introduced a whole new deep linking API called Universal Links. Ever since then, deep linking in iOS apps is commonly referred to as universal links.
What Is Deep Linking in Android?
Just like Universal Links, deep links in Android are commonly referred to as Android App Links.
Types of App Deep Linking
1. Standard Deep Linking
It is the most straightforward form of app deep linking and is also referred to as universal links. Standard deep linking works only if the user has already installed the application and directs users to a specific part of the app.
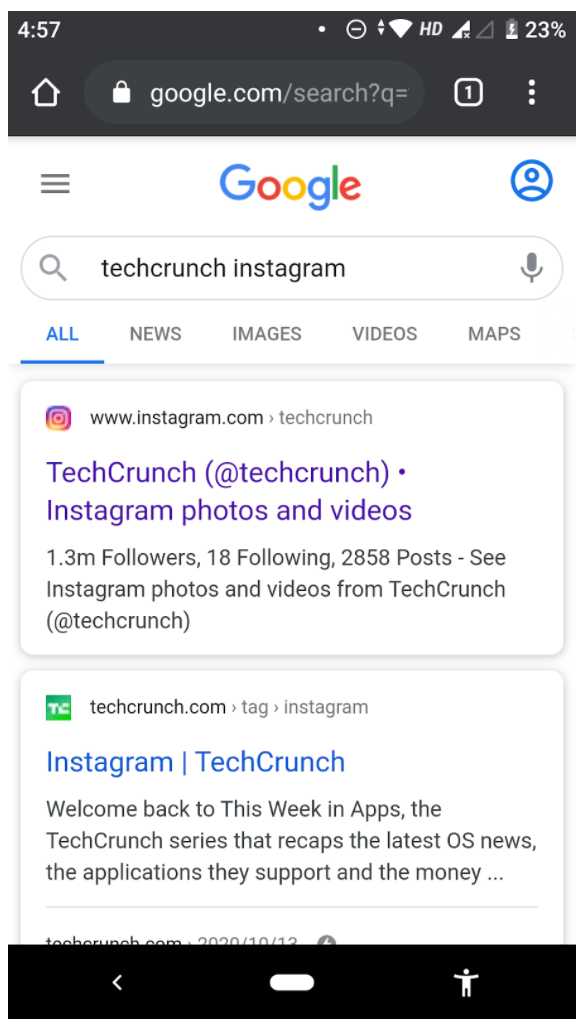
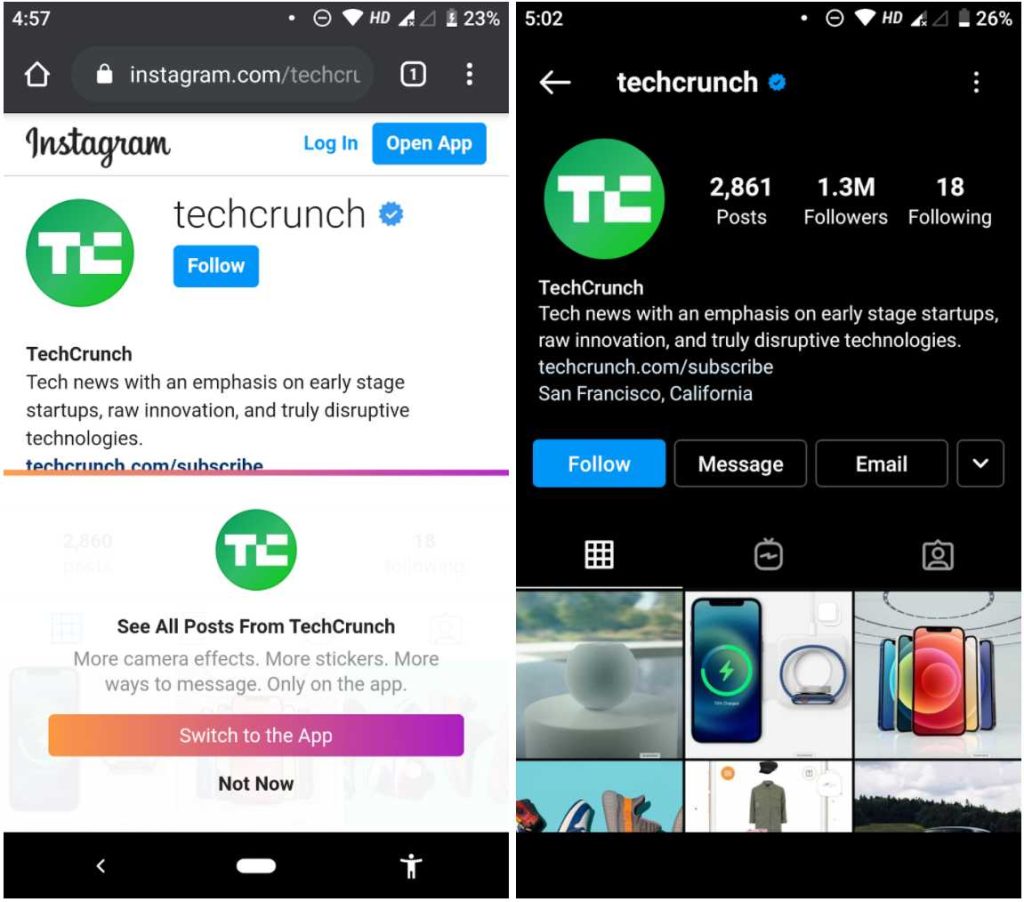
If the app isn’t installed, the user may be shown an error, redirected to a fallback page, or introduced to the browser version of the app, if available. Here’s an example of Instagram.
If the Instagram app is installed, users are forwarded to the Instagram page of TechCrunch. Or, the browser version of Instagram is opened.
Standard deep links are also referred to as default links. They are beneficial for retargeting campaigns – where marketers are particularly interested in finding users who have already installed the app and want them to return and engage.
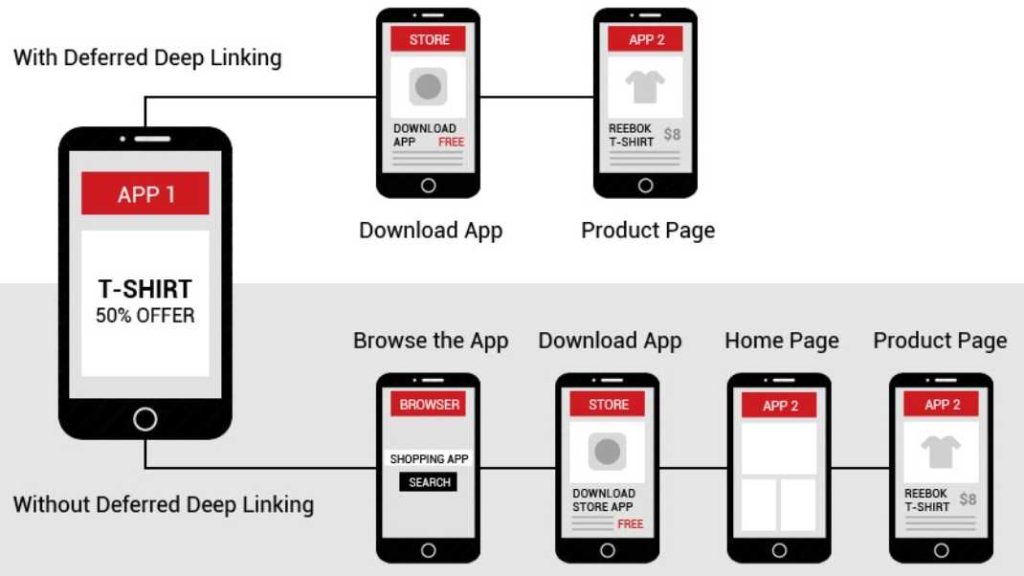
2. Deferred Deep Linking
Deferred deep linking is the perfect choice for app user acquisition. Unlike standard deep links, deferred links will direct users (without the app installed) to the download page.
If not for deferred links, deep link to app stores will be similar to any other link, and once the app is installed, it wouldn’t know that it was accessed using a deep link. This is because app stores don’t pass the referral links utilised by the user to install the application.
Deferred deep links eliminate such inconsistencies and will forward the user to the specific app content once installed.
3. Contextual Deep Linking
Contextual deep links are known to double the rates of in-app signups. In essence, contextual deep links serve the functions of both standard and deferred links. But it holds more information than the other two.
 The onboarding process differs based on the platform the contextual link was clicked on. Image Credit: neilpatel.com
The onboarding process differs based on the platform the contextual link was clicked on. Image Credit: neilpatel.com
Along with passing information regarding the in-app location where the user needs to be redirected, contextual deep links contain extra information such as,
- Who the user is.
- Who referred them?
- From which platform were they referred.
- The promo code that enticed the user to install the app, which should be applied on the check out screen.
Contextual deep links allow app creators to offer personalized and highly-targeted app onboarding experience. Since an effective onboarding process can boost the retention rate by 50%, if you haven’t utilised contextual links, you are missing out a lot.
Why Mobile App Deep Linking Matters?
1. It Enhances the UX
With the help of app deep linking, developers and marketers can lead a user to a specific section of an app, without the need for navigation. As generic screens like home screens are removed from the equation, users can experience highly specific and targeted content in no time.
2. It Makes App Indexing Possible
App indexing allows search engines like Google to index apps just like websites. This means if a user is searching for particular content, along with other web pages, Google will display your app if it contains the relevant content.
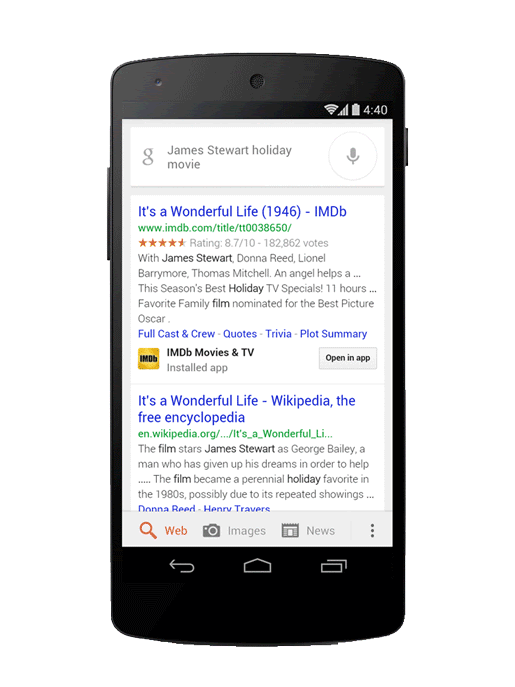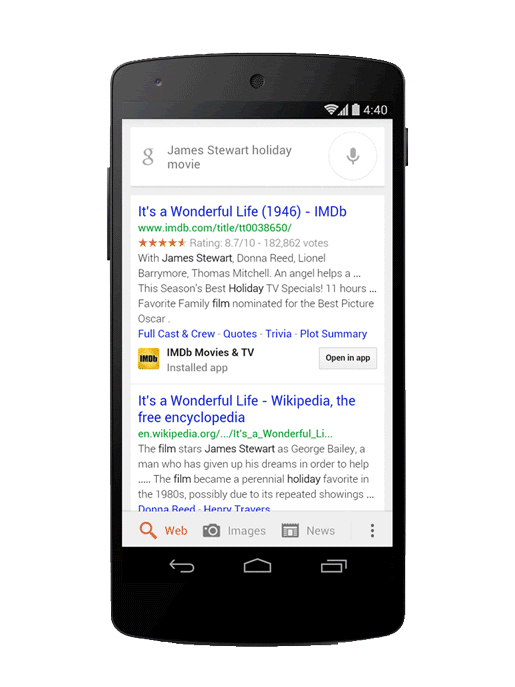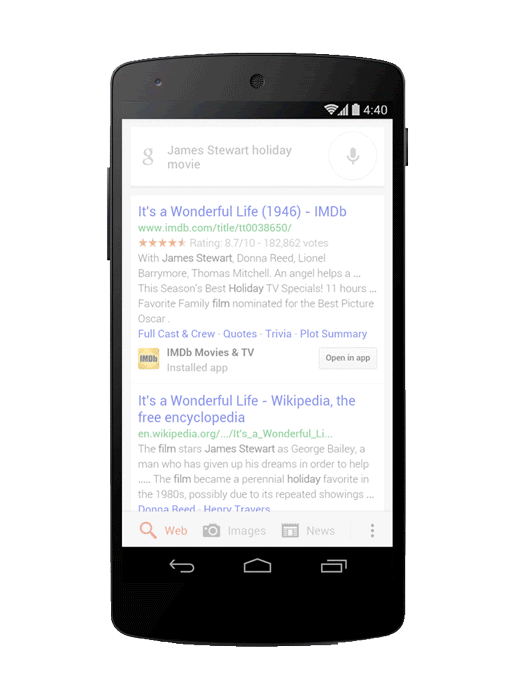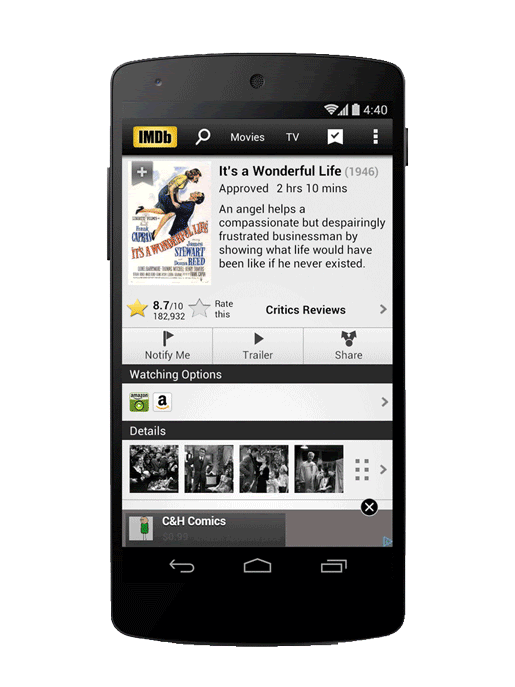 App indexing increases the discoverability of apps. Image Credit: searchengineland.com
App indexing increases the discoverability of apps. Image Credit: searchengineland.com
It is an excellent strategy to enhance discoverability and user acquisition and is made possible by app deep linking to specific app content.
3. It Enhances App Onboarding
Deep links allow you to offer a personalized app onboarding experience to users. With the help of contextual deep links, you can send out customised app invites, along with incentives or rewards. As 39% of users spend more with a mobile coupon, contextual deep links become more important for revenue generation.
4. It Makes Things Easier for App Marketers
Insights are the holy grail when it comes to app marketing. Although app analytics tools are invaluable to gain insights, deep links will make things even better. With deep links, app marketers can obtain insights regarding how a user opened or installed the application.
5. It Increases Retention and Engagement
 The difference in activation rate with normal and deep links. Image Credit: techcrunch.com
The difference in activation rate with normal and deep links. Image Credit: techcrunch.com
Deep links are known to double the in-app signup, and retention rates and users who installed an app using deep links visited twice as frequently as regular users.
6. It’s Useful for Re-engagement
Like the example of Netflix previously mentioned, marketers can use deep links to send out push notifications and emails containing exclusive in-app purchase deals or specialised incentives to re-engage users.
How Do You Create a Deep Link?
Before looking at how to create app deep linking, there is another term you need to be aware of – URI schemes. They are schemes that make deep linking possible and are similar to website URLs that redirect you to a specific page on a website. Here’s an example of how they look.
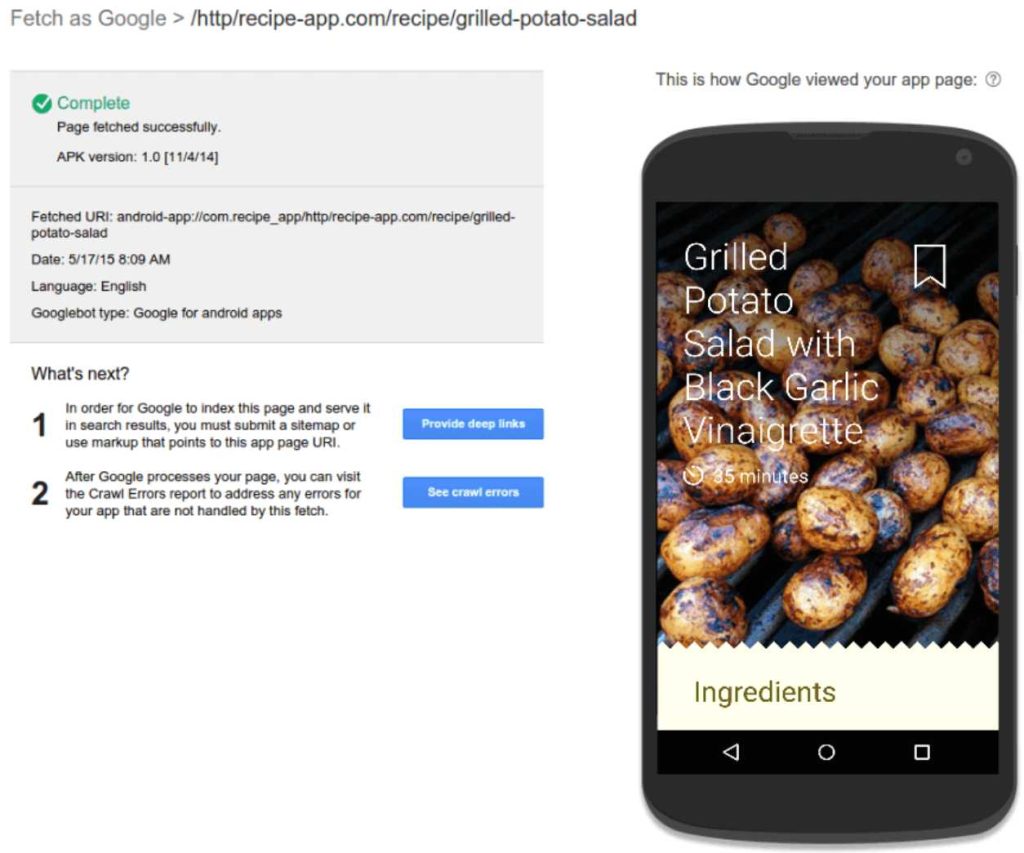 Image Credit: searchengineland.com
Image Credit: searchengineland.com
URI schemes follow the format appname://path/to/location. Developers can set up custom URIs to forward users to specific app content. Now, let’s take a look at how deep links are created for the dominant mobile operating systems, Android and iOS.
Android App Deep Linking
Android smartphones have three options to select from when a URI is requested.
- Using the URI, open a preselected application.
- Open the only available application that can handle the URI.
- Prompt the user to pick an available application.
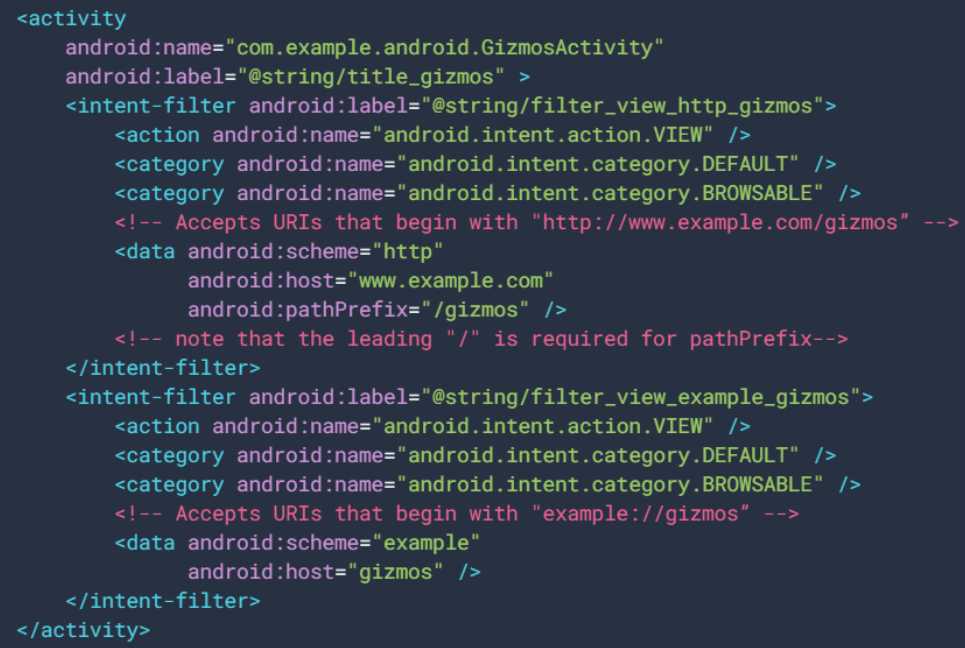
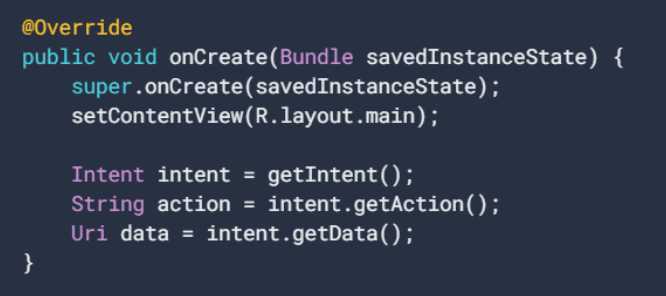
To add deep links, you have to open the AndroidManifest.xml file of your Android app. Then using an intent filter, you have to add the following elements.
- Define the ACTION_VIEW attribute in the <action> element.
- <data> tags which hold the URI scheme, host, and path.
- CATEGORY_DEFAULT and CATEGORY_BROWSABLE attribute in order to move a user from a browser to the application.
Here’s an example of how the code will look like.
Once that is completed, you need to make sure that your application can read the data from the created intent filter. This can be performed by adding getData() and getAction().
To know more, check out Android’s official documentation on deep linking app content.
iOS App Deep Linking
App deep linking in iOS is enabled through Associated Domains Entitlement. It is a method of notifying search engines about which app belongs to which website. Using this technique, when a user clicks on your website, you can choose what type of deep link it will activate.
You also have to add an Apple App Site Association file to your site to verify it. The association file must contain the following code.
After that, you need to update your app delegate (which is similar to the manifest file of Android apps) to respond appropriately while receiving the NSUserActivity object.
To know more, check out Apple’s official documentation on deep linking.
Mobile Deep Linking Examples
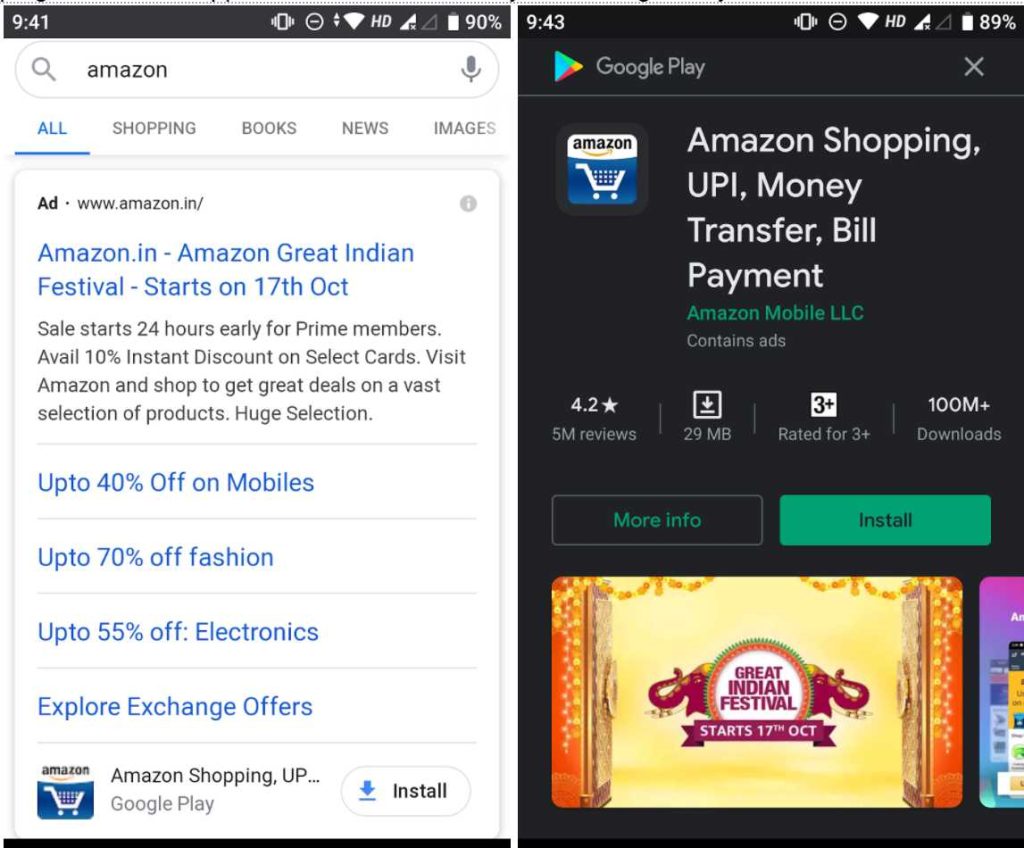
1. Amazon
Tapping on Amazon app install button redirects you to Google Play.
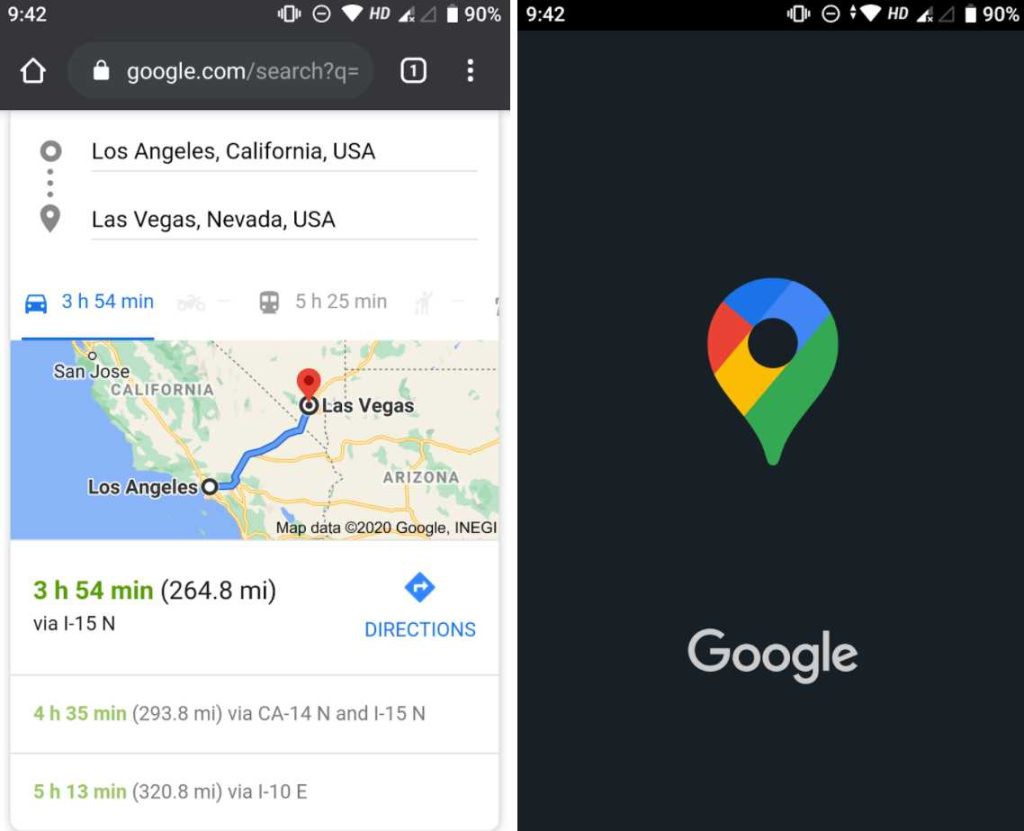
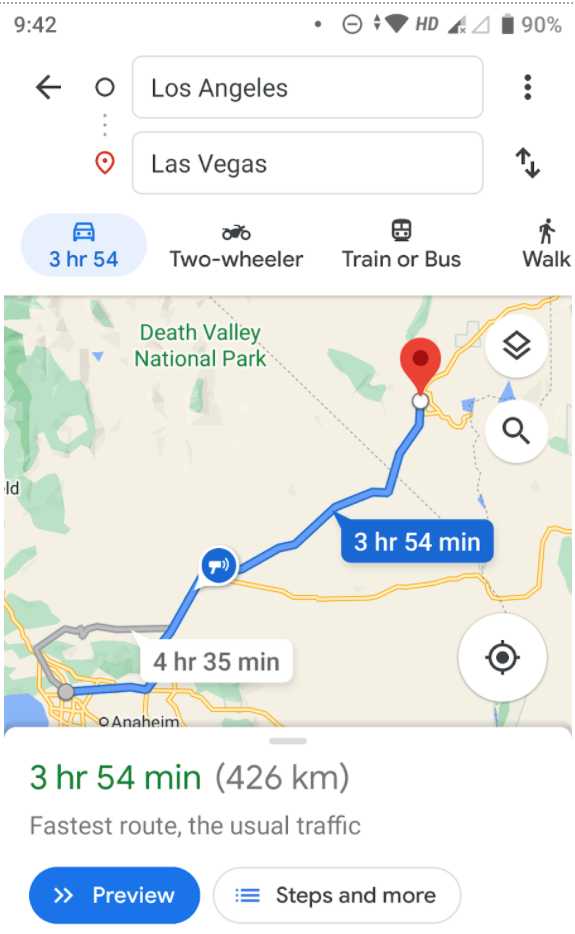
2. Google Maps
With app deep linking, Google redirects users searching for routes to Google Maps.
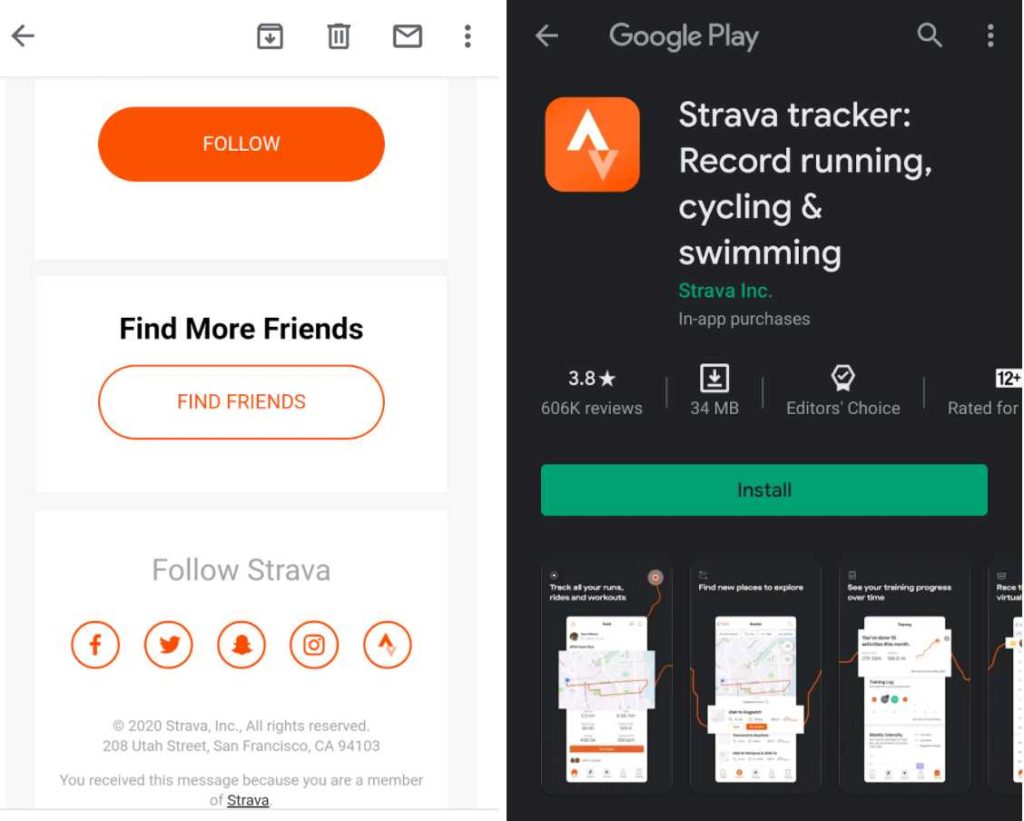
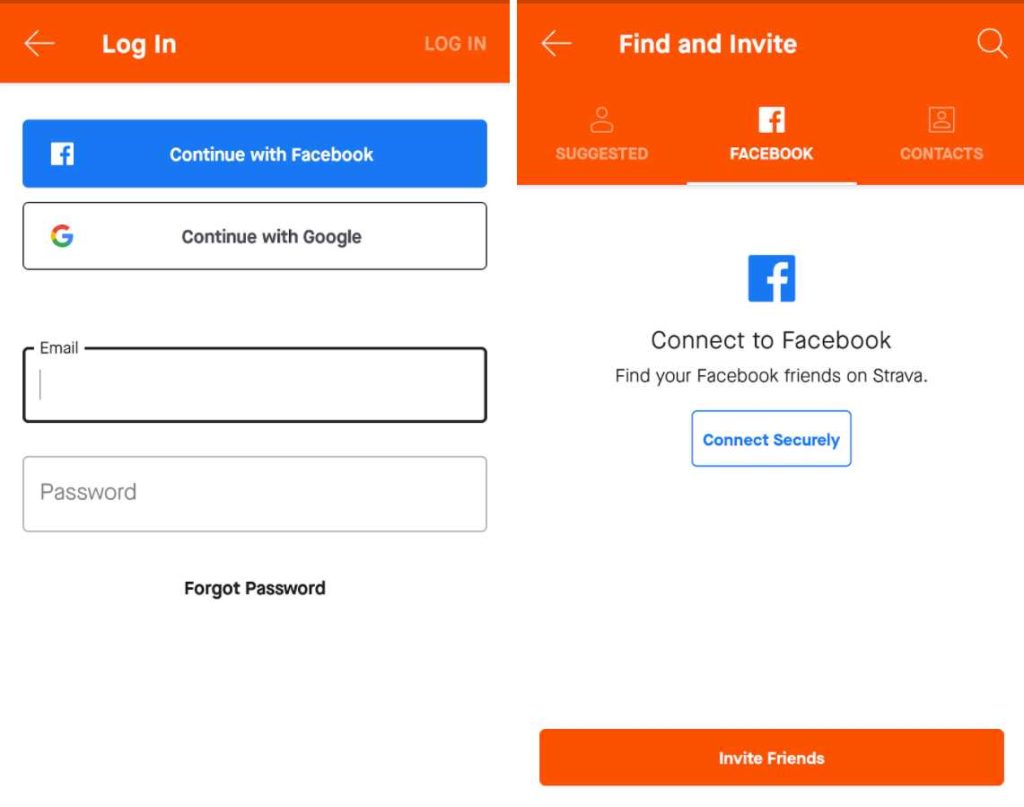
3. Strava
When clicking on the CTA, users are redirected to the appropriate app store to download the app, if not installed. Then after the log-in, the user is forwarded to the app section to connect with friends – an example of deferred deep linking.
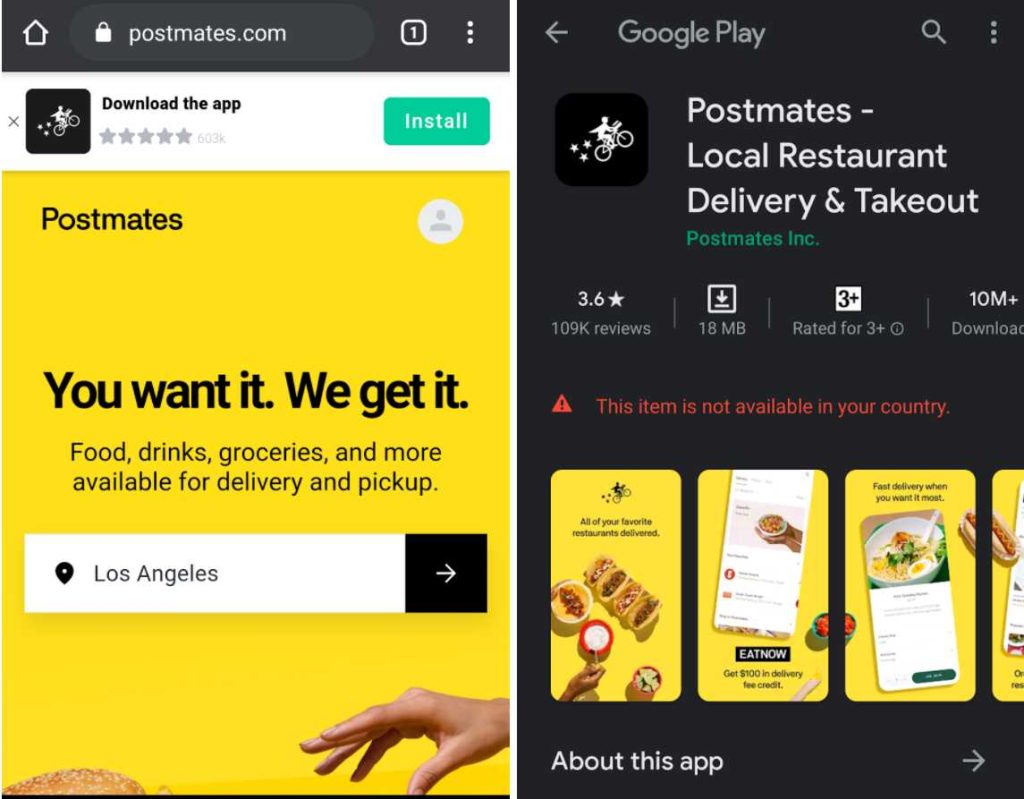
4. Postmates
Deep linking is beneficial for mobile app promotion via websites. If your website ranks high in the search results, you can use deep linking as a cost-free method to drive installs. You can also offer discounts to install an app and with the help of deferred links, once the app is installed, the discount coupon will be auto-applied.
5. Duolingo
Another example of deferred deep linking. By clicking on the CTA of email from Duolingo, users are redirected to a particular lesson.
 Without the app, Duolingo redirects to its mobile website (left).
Without the app, Duolingo redirects to its mobile website (left).
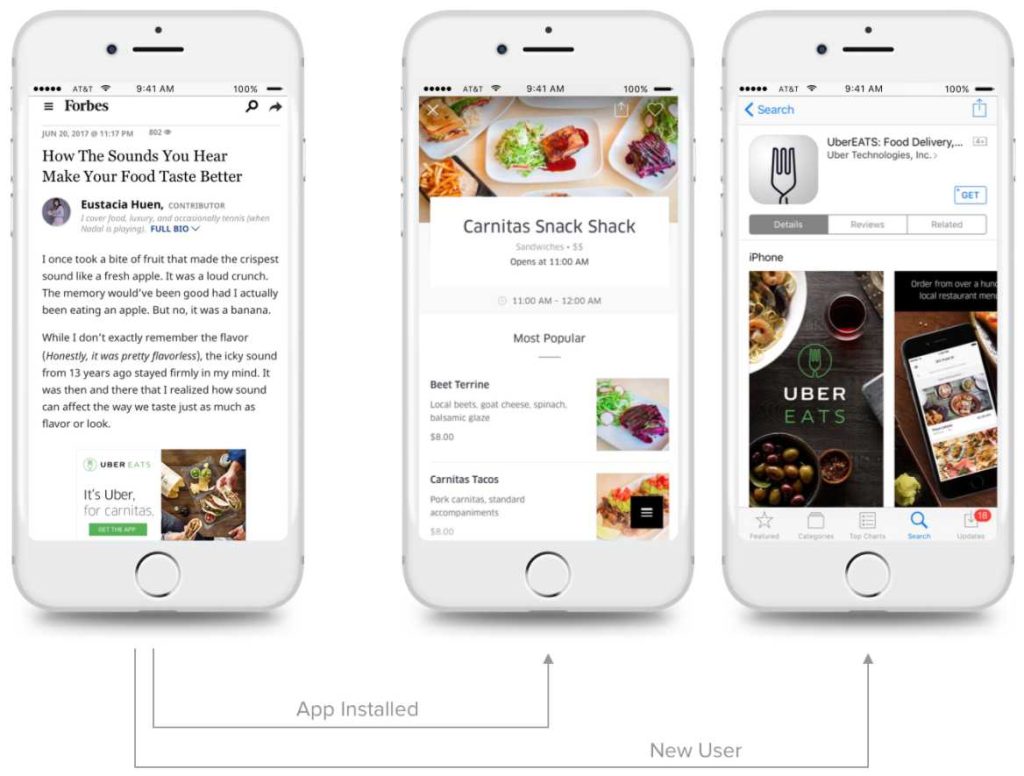
6. UberEATS
Deep linking is useful while displaying app install ads.
Conclusion
App deep linking must not be an afterthought but a part of the mobile app development process. Since it puts the users on an alternate path, away from the usual user flow, you must ensure that the architecture and information hierarchy of the app complements it.
Along with driving user engagement, deep links are useful for marketers to track and optimize their app marketing efforts. With deep linking, marketers can identify the app campaigns that were convincing enough to drive installs and also were able to readily showcase the value of an app.
Deep links also give marketers the ability to better understand the difference and significance of different groups of target audiences. This information can be used to find the optimal cost of acquisition and for targeting the users with the highest lifetime value.