Table of Content
Regularly acquiring users with high lifetime value is a mobile app developer’s dream come true.
Apart from app marketing strategies like app install ad campaigns, cross-promotion, or influencer marketing, one way to make this a reality is by improving your app’s online visibility and ranking higher on search results.
In the case of websites, the process of increasing ranks on search results and driving more traffic to them is known as search engine optimization (SEO). When talking about mobile apps, the same process, although aimed at driving installs instead of traffic, is called app SEO.
It’s a user acquisition strategy that can drive installs even if you stop doing it – unlike paid campaigns. In this article, we’ll discuss more about mobile app SEO, how it’s different from app store optimisation (ASO), and the best ways you can do it.
What Is App SEO?
App SEO is all about making your mobile app visible in search engine results. It’s the optimization strategies that can help in driving installs from the search engine results page (SERP), whenever a potential customer searches for your app or a specific feature it offers.
One in four app users discovers apps using search engines – making mobile app SEO optimization a necessity rather than a choice.
As Google is the most popular and used search engine in the world, we’ll be talking about SEO in its perspective. Also, many often confuse app SEO with app store optimization (ASO). We’ll discuss in a bit how both are actually different.
 Search ad for an app listed in Google Play.
Search ad for an app listed in Google Play.
Of course, you could always run PPC campaigns to drive app installs. It’s an excellent strategy to acquire users quickly, and in fact, 50% of app installs due to ads come from search ads. But it isn’t organic, and your results will diminish as soon as you stop the campaign.
App SEO vs App Store Optimization
It’s safe to say that app SEO and ASO are two different sides of the same coin.
While app SEO means the optimization of apps to rank higher in the results of search engines like Google or Bing, a part of ASO means the same for app stores. In that sense, ASO can also be referred to as app store SEO.
However, ASO is performed not just to satisfy the search algorithms. Instead, it’s also focused on enticing users to download and install your application.
But the majority of implementations for both forms of optimization are performed inside app stores. We’ll get to that part in a while.
Performing ASO is equally essential as crafting a remarkable app UI design. Only if people discover your app will they install it. And ASO is not just about discoverability. It’s more like a sales pitch and how creative you’re in doing it will invariably affect the number of users who click, install, and try your app.
If you’d like to know more about app store optimization strategies, how it’s performed and its do’s and don’ts, check out our practical guide on app store optimization. Also, most of the app SEO strategies will be automatically implemented if you rightly perform ASO.
How Apps Appear on the SERP
Before looking at how to improve mobile app SEO, take a look at the ways your app will appear on the SERP.
1. App Pack
App pack is a group of apps suggested by Google. It appears on the mobile SERP and is an exclusive mobile-friendly feature. It typically contains three to six apps that are relevant to the search query and in most cases, is featured at the top of the SERP.
Generally, an app pack will contain,
- App titles
- Ratings
- Number of reviews
Users can also tap “More apps” and view an extended list of 30-100 related apps. App packs are device-specific and OS-specific and link directly to the app store product page of the respective mobile operating system.
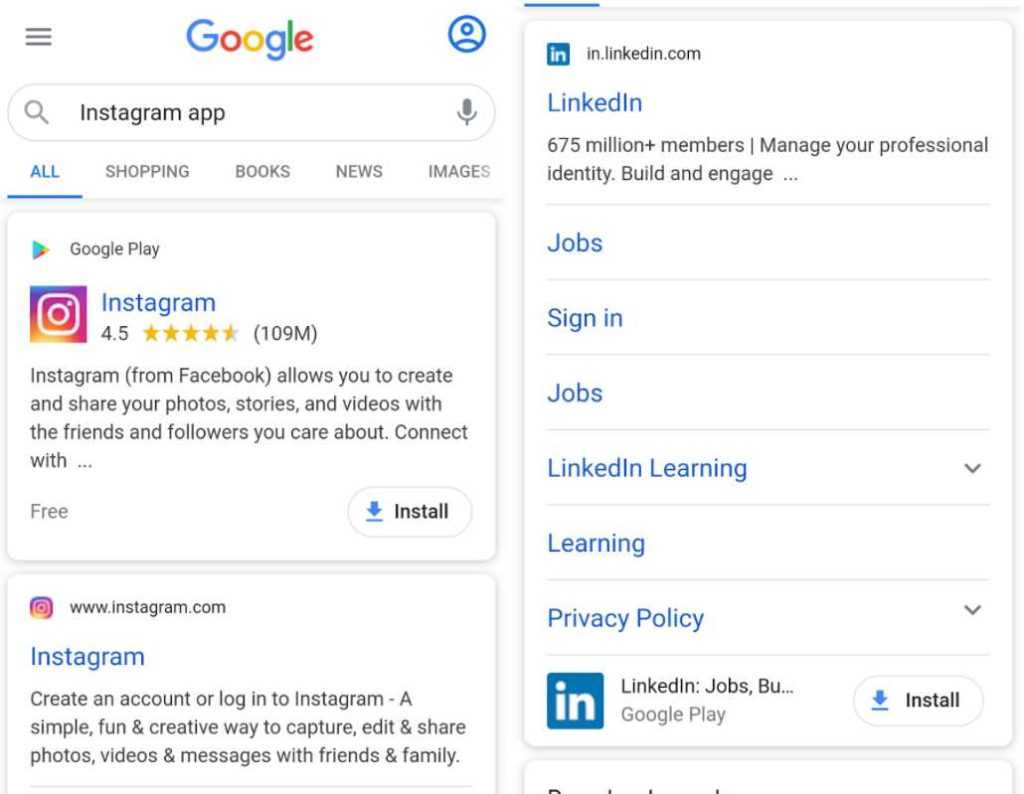
2. Single Results
If someone searches for your app’s name, a preview of your app store product page may be shown in search results in a snippet format.
Generally, such a snippet will contain,
- App title
- Ratings
- Number of reviews
- The first line of the long description.
The snippet will also contain a download button that redirects the user to the product page in Google Play. Google is yet to include Apple App Store app page redirects for iOS devices.
3. App Indexing
 Clicking on the search result takes you directly to the specific app section.
Clicking on the search result takes you directly to the specific app section.
By the process of app indexing, Google crawls internal app sections and screens. This is useful for users who have already installed the application and want to find or visit specific app content or sections by searching it on Google.
By clicking on the search results, if users have installed the app, they can visit specific app sections via app deep links. Even if they haven’t installed the app, deferred deep links can redirect users to the respective app store and once the application is installed, will take them to the specific in-app section.
Along with increasing the engagement rate, app indexing is equally useful to acquire new users as whenever an individual searches for particular content, your app might be presented.
Additionally, app indexing is considered as a ranking signal by Google (for Android users), and so, you don’t want to miss out the opportunity to rank higher and expand the user base.
To get your mobile app’s content indexed by Google, you need to use the same URLs in your app that you use on your website. Then, you need to verify that you own both your mobile app and the website. Check out app indexing on Google Search to view the steps in detail.
How to Perform App SEO
Just like in ASO, the factors that affect your app’s ranking can be grouped into two categories – on-metadata and off-metadata factors.
In short, on-metadata factors can be modified and are under the control of app publishers. On the other hand, off-metadata factors can’t be altered and aren’t under the control of publishers.
App title, description, and keyword list are examples of on-metadata factors.
The number of installs, engagement rate, reviews, and ratings are examples of off-metadata factors.
Here are some solid steps you can take to drive more installs with the power of mobile app search engine optimization.
1. Create a Great App
This might seem like a no-brainer, but the efforts you put in the mobile app development process will directly affect your SERP rankings. That’s because the engagement rate is a critical off-metadata factor, and if you build an app that wins hearts, Google will automatically bring it up.
Of course, once you’re done with creating an enjoyable mobile app, you need to offer a comprehensive and fun onboarding experience to tempt more people to sign-up and recognise the true value of your app.
2. Conduct Keyword Research
Depending on your target audience, features, similar apps, and category of your app, you need to brainstorm keywords. You also need to consider the top keywords people search on Google as they can be slightly different from what’s searched on app stores.
Frequently searched queries on external search engines may be coupled with OS or device-specific terms, for example, “Android running app” or “iOS expense tracker”.
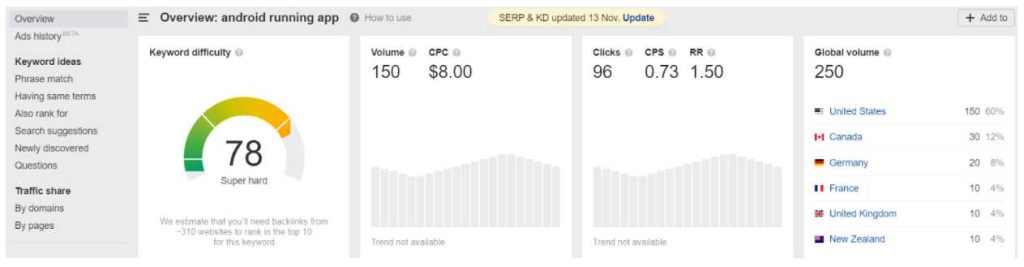 Ahrefs estimates that the keyword “Android running app” receives 250 searches per month.
Ahrefs estimates that the keyword “Android running app” receives 250 searches per month.
You can make use of app SEO tools like Sensor Tower, TheTool, or App Annie to find your competitors’ keywords. You can also use tools like Google Keyword Planner or Ahrefs to find relevant keywords for search optimization.
3. Optimize the App Title
 “Learn English Free” is a high volume keyword included effortlessly by Duolingo.
“Learn English Free” is a high volume keyword included effortlessly by Duolingo.
The app name must clearly depict what the application is about and must also include relevant keywords.
Although the steps to rightly craft the perfect title, description, and other on-metadata factors are fully explained in our ASO guide, as a rule of thumb, try keeping it short and memorable with relevant long-tail keywords.
Along with optimizing the title for app stores, it must be optimized for Google search – meaning, you must try including certain (extra) keywords that may not be relevant to app stores. Also, make sure you don’t overdo this process as app stores will penalise you for keyword stuffing.
4. Optimize Descriptions
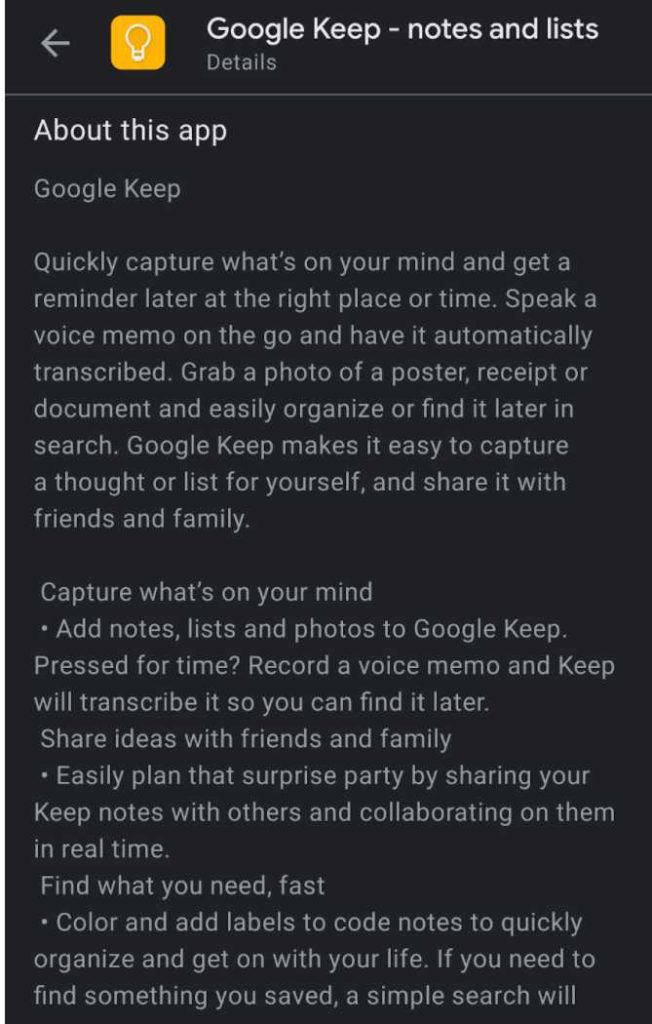 The long description of Google Keep app in Google Play.
The long description of Google Keep app in Google Play.
For Google Play, both short and long descriptions are critical for ASO, and their keyword optimization can affect your app’s ranking. However, the same is not true for the App Store, and the 4000-word limit description exists to provide users with more information about the app.
However, in terms of Google Search and App SEO, keyword optimization of descriptions are vital for both app stores. Google will crawl these descriptions and so, optimizing them will help you rank higher in SERP.
5. Optimize URL
URL is a critical on-metadata factor that will affect your app’s ranking in search engines as well as app stores. Try including relevant keywords in it but do note that once you publish the app, you can’t edit the URL again.
6. Gain Quality Backlinks
Just like in website SEO, acquiring quality backlinks is crucial for mobile app SEO. Backlinks will enhance your app’s authority and therefore, will help in ranking higher on search results. You can request high authority review websites like Mashable or TechCrunch to review your app and link to it.
You can also utilise link building strategies such as guest blogging, paid promotions, and content repurposing to drive traffic and quality backlinks.
Best Practices to Win App SEO
1. Rely on Other Marketing Strategies
The number of downloads is a complementing factor for app SEO. The higher the number of downloads, the better. Therefore, investing in other marketing strategies will help in boosting your app’s search rankings.
To begin with, you can try app marketing strategies such as,
- In-app ads
- Influencer marketing
- Social media ads
- Search ads
- Push notifications (to increase engagement rate)
- Cross-promotion
2. Use Website SEO to Complement App SEO
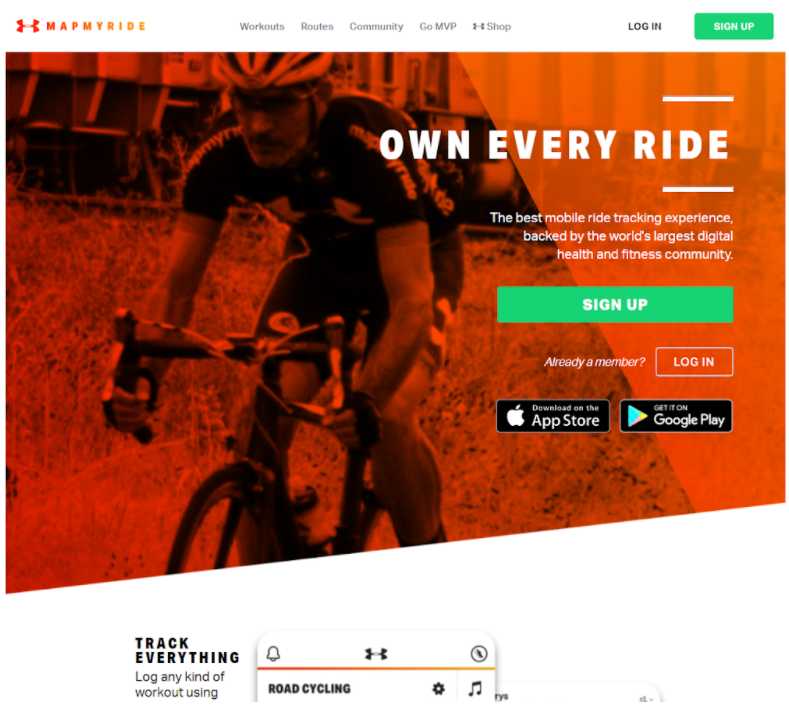 The website of the MapMyRide app.
The website of the MapMyRide app.
Since setting up a website to promote your app is a top priority app marketing strategy, you can optimize it for search and drive more traffic – which will ultimately translate to higher app installs. In that sense, you can focus on your website’s SEO to enhance your app SEO.
Since quality backlinks can affect your app’s ranking, becoming a thought-leader in your niche by adopting content marketing strategies such as blogging, social media marketing, and video marketing will be beneficial.
You can also set up specialised landing pages that will highlight the noteworthy features of your app along with a call to action (CTA) to visit the app store product page.
3. Frequently Roll Out Updates
Although it isn’t advised to frequently modify and update your ASO components, it’s highly recommended to frequently roll out app updates. Frequent updates will give users the impression that you care about them and their concerns.
Perfecting the app will also improve its performance and reduce the crash rate – which will directly affect the engagement rate and social desirability of your application. Frequent security updates will also give users more confidence in using the app.
4. Use App Related Keywords
If you wish to rank in Google app packs, then consider including app-related keywords such as “running app” or “2D gaming apps”. That’s because when searching for apps in app stores, users are least likely to use the term “app” in the search query. But the same isn’t true in search engines like Google.
5. Include an In-App Feedback Section
 Feedback section of the Wix app.
Feedback section of the Wix app.
If users have no means to communicate with you about unpleasant in-app experiences, they’re more likely to post them as reviews on app stores. This will not only reduce the click-through rate but will also harm the search rankings. Try including an in-app feedback section to keep certain things between you and the customer.
App SEO Is a Journey Without a Destination
Just like web SEO, app SEO must be continually performed to gain the best results. Since Google frequently changes and updates its search engine algorithms, you can’t ever be done with app SEO optimization.
The key is to experiment and A/B test all on-metadata factors and also get inspired from your top competitors. Since user experience and satisfaction and app store reviews are critical factors that can decide app store rankings (and ultimately SERP rankings) start perfecting your app from the inside to complement each mobile marketing campaign.