Table of Content
Loyal customers play an essential role in improving business performance and promoting competitiveness amongst enterprises. Furthermore, loyal customers can significantly help reduce companies’ publicity and advertising costs while also helping attract more new customers with the herd mentality.
One of the concepts that come into play when dealing with customer loyalty is churn, which is the topic of today’s discussion. So, let’s delve in, shall we?
What Is Exactly Churn?
Generally speaking, churn is essentially a phenomenon where customers or users no longer utilise or buy products or services of a business for various reasons.
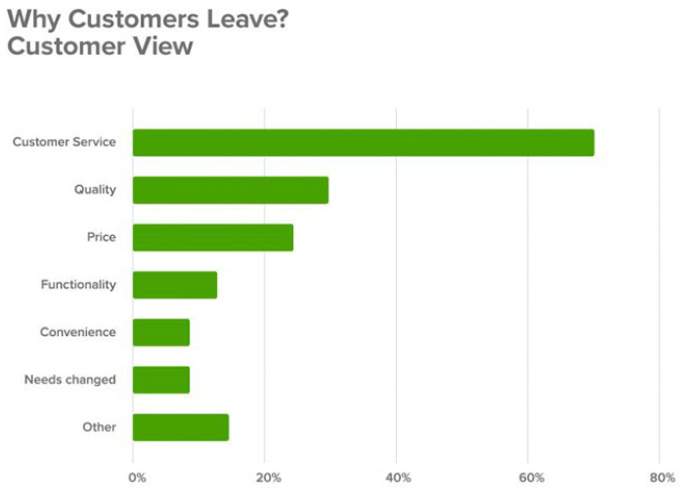
Why Customers Usually Churn?
There are two primary reasons why customers churn:
- Users or customers choose to churn because they are not getting the value they needed or their interest changed
- Users/customers can churn involuntarily (or “passively”)
Let us better explain these reasons with more context.
- Consistently unmet expectations as users or customers feel let down when companies do not deliver on a specific promise. As a result, they are quick to head for the door and let their disappointment be known to anyone willing to listen.
- Poor customer service: In practice, every customer wants to be treated with courtesy and priority. Poor customer service is an easy way to trigger customers to churn.
- Not enough value: With a plethora of options in the market for customers to choose from, value is a vital differentiating factor for brands. Unfortunately, when customers do not feel they are getting value from a brand, they are quick to try one of the multiple other options at their disposal.
- Poor brand loyalty as customers easily leave at the next opportunity to try other offers at a lower price, or even with a fancier widget.
What Is Churn Rate?
Also called attrition rate, churn rate is basically a measure of the number of customers or users who leave a business or mobile app during a given period. It can also refer to the revenue lost as a result of such departures.
As such, a high churn rate indicates that something about your product or service is not appreciated by people, or did not meet their expectations when they signed up. Maybe something is broken, delivering a poor user experience or simply not delivering as advertised. Maybe your product or mobile application is too confusing to customers.
 Net negative revenue churn. Image Credit: baremetrics.com
Net negative revenue churn. Image Credit: baremetrics.com
In terms of mobile marketing, a high churn rate could signal overarching problems with your product, mobile application, website, pricing model, customer support, design, or even user experience (UX). So, a high churn rate alerts you to the fact that you are incrementally losing customers, but it will not necessarily explain why. However, to get the most out of churn rate, it is sometimes advisable to consider using a cohort analysis, which we comprehensively discussed in this blog.
Calculating Customer Churn
A good way to understand the impact churn has on one’s business is to basically calculate their user/customer churn rate. The formula to achieve this is pretty straightforward, it essentially involves dividing the number of customers lost in a specific period of time by the number of customers present at the beginning of the time period to arrive at a percentage.
Churn rate = (the number of churned subscribers/the total number of subscribers) x 100
So, to calculate churn rate, take these steps:
- Determine a specific time period.
- Determine the number of customers acquired in this specific time period.
- Determine the number of customers lost or churned in this time period.
- Divide the number of lost customers by the number of acquired customers.
- Multiply that number by 100.
Subsequently, derived churn rate can then be utilised to calculate:
- Number of customers lost
- Value of recurring business lost
- Percentage of recurring revenue lost
For instance, if you desire to measure the churn rate for a 500,000-user mobile application and you know that 15,000 users left in June, you shall record a 3% monthly churn rate.
While churn rates might fluctuate from month to month or even dependent on the campaign, if your churn continues at 3% every month, then your overall churn rate will be 36% a year, or 180,000 users will have been lost. This, in turn, can also translate into a substantial amount of revenue lost.
 How to calculate churn rate. Image Credit: towardsdatascience.com
How to calculate churn rate. Image Credit: towardsdatascience.com
What Is Churn Prediction?
Churn prediction revolves around identifying customers who are most likely to discontinue using your mobile app or a service, and is an important metric for many firms in multiple different industries.
In marketing analytics, churn prediction employs techniques drawn from machine learning and predictive modelling to estimate the likelihood that customers will churn; as well as techniques from time-series forecasting and regression analysis to predict the future churn rate for a segment of customers.
 How to predict churn the right way. Image Credit: towardsdatascience.com
How to predict churn the right way. Image Credit: towardsdatascience.com
Why Predict Churn?
To maximise return on investment, marketers typically extend discounts or incentives to customers that are at risk of churning, or most unlikely to make a purchase. By predicting the likelihood of churn for each mobile user, mobile marketers can segment their user base and target specific marketing communications to those particular segments that they deem eligible for discounts.
As such, marketers can promote discounts or other offers without indiscriminately spamming loyal users, or incurring costs associated with offering a discount to mobile users who didn’t really need it to continue their relationship with the brand.
Furthermore, forecasting the churn rate can be useful in tweaking product strategies — from pricing, to packaging, to adding or even removing specific features that will impact their key performance indicators (KPIs) such as, revenue and profitability.
Additionally, by predicting a future churn rate utilising time-series forecasts, mobile marketers can get a very quick read of how changes are impacting user behaviour, then act to either change what they are doing or keep things the same.
Churn Statistical Metrics
As we have established, churn is a vital metric to measure for all brands and businesses; however, predicting churn is even more impactful. Predicting how likely a user is to churn and when they will churn allows mobile marketers to preemptively engage them with relevant offers.
However, because people can stop being users for any number of reasons, it makes predicting churn extremely difficult. This is where machine learning(ML) and data science come into play to help make churn predictions by identifying obvious and unobvious attributes of user behaviour.
Two particularly helpful metrics for mobile marketers to understand churn prediction are Churn Time and Churn Score.
Churn Time
Churn Time is essentially a statistical metric that predicts the number of days from the current date that a given user will likely stop using a mobile app or making purchases. This model considers signup date, date of purchase, date of engagement, and other time- and date-based attributes to define the lifetime of a customer.
Overall, this metric is crucial since it basically estimates how much time is left until a given user/customer will stop making purchases. Furthermore, by amalgamating business-specific knowledge about churn definitions with this model, mobile marketers can better understand customer lifetime length on a more individual level.
Churn Score
A churn score is basically a statistical metric that forecasts the churn state of a given user/customer. It fundamentally takes into account purchase history, demographic information, website and email activity, in combination with churn time, to figure out whether a customer is at risk of churning, or not.
So, this particular metric is critical since it gives a mobile marketer the signal that a specific customer needs to be engaged immediately to prevent them from churning.
As such, marketers can then specifically target these potentially ‘churned segment’ with a win-back campaign or other engagement tools. Understanding the Churn Score of each segment can also be a useful way to figure out how to allocate marketing efforts and determine which campaigns achieve higher ROI.
How to Reduce Churn Rate
In essence, to reduce churn rate, one must first understand why user/customers churn as it can either be voluntary or involuntary. In practice, voluntary churn occurs when users/customers cancel their subscriptions on their own. On the other hand, involuntary churn occurs when subscriptions get cancelled because of certain situations, such as, not updating payment information.
 Ways to reduce customer churn. Image Credit: intellias.com
Ways to reduce customer churn. Image Credit: intellias.com
Generally speaking, the best approach to controlling and reducing churn is proactively managing customer relationships. In this sense, there is really no silver bullet, but a few mechanisms and techniques can be employed to maintain a ‘healthy’ churn. For example, mobile marketers can:
- Define and separate their most valuable users/customers from all the rest and ensure to make them happy since they generate the most revenue.
- Consistently analyse churn beyond numbers, by always digging deeper, and exploring why they are so.
- Strengthen the user/customer journey by traversing varied processes to improve customer experience.
- Support their customers with materials to keep customers comfortable, informed, and engaged.
- Continuously fine-tune and foolproof their targeting strategy.
- Employ user complaints to their advantage
- Define their advantages and find what makes their uniqueness visible.
- Provide excellent customer support services that are friendly and helpful, to improve customer satisfaction—for example, fast responsiveness and successfully resolving customer queries.
- Build easy to navigate interfaces that do not overwhelm customers
- Continuously offer great deals, packages and bundles to attract new customers and keep old ones consistently valued.
Conclusion
In summary, churn is an essential important metric on its own that provides true value for mobile marketers. In practice, knowing which users/customers are likely to churn and when they are most likely to do so helps mobile marketers react more quickly to retain them.
However, it’s imperative to realise that the best way to address churn is to actively work on preventing it. Overall, customer churn rate is a ‘quantitative’ metric that occurs for ‘qualitative’ reasons. Fortunately, machine learning and data science can programmatically utilise quantifiers to act as signals for these qualitative reasons (such as purchasing behaviour, email/ onsite activity).
All things considered, a zero-churn rate is virtually impossible, unless you possess the perfect product or mobile app! That being said, you can still minimise churn rate by meeting and exceeding user customer expectations and employing technological tools that help monitor churn and reduce cancelled subscriptions.