Table of Content
Push notifications are one of the most cost-effective app marketing strategies you could adopt. It’s an excellent method to engage and retain users and can significantly enhance the lifetime value of mobile apps.
Push notifications are messages sent by an app publisher to a user’s mobile phone. It could be sent at any time, and users don’t have to be using the app or their device in order to receive one.
The message could be about anything depending on the nature of the mobile app – latest deals, utility messages (weather or traffic reports), fluctuations in the stock market, location-based ads, expiring coupons, or the latest news.
In this article, we’ll discuss how push notification works in Android and iOS devices.
With an opening rate of 90%, push notifications are one of the best methods to increase app loyalty and revenue. If you want to know more about what push notifications are, its examples, when and why you should use them and the best practices to use it for enhancing app loyalty, check out our quick guide on push notifications.
 An Android push notification example. Image Credit: positronx.io
An Android push notification example. Image Credit: positronx.io
How Are Push Notifications Different From SMS and Email
 SMS message vs email vs push notification. Image Credit: pushmaze.com
SMS message vs email vs push notification. Image Credit: pushmaze.com
First off, SMS and emails can be caught and annihilated by spam filters or may lose relevance among other messages. But push notifications go straight to the users’ notification centre (or notification bar). They remain there as long as the users don’t swipe them off or in some cases, till the device shuts down or restarts.
Also, the opt-in process for push notifications is hassle-free. Users don’t have to input their personal information like phone numbers or email addresses. All they have to do is tap the “Allow” button, and app publishers can continuously keep in touch with them.
If you were to execute an SMS campaign, you’d be charged for each SMS you send, and so, the process can be incredibly expensive. In the case of push notifications, you can send out as many as you like, but at the expense of your users’ tolerance.
The same is in the case of email marketing campaigns. You’ll have to spend an hefty amount on it and if you’re unlucky (and spammy) your efforts will often end up in the spam section. Also, users might also submit fake or temporary email IDs to gain the reward you offer for subscribers.
Since push notifications are sent by confirming the registration ID (discussed later), users can’t submit fake subscription information like a fake email ID.
Another interesting aspect of push notifications is their customizability. You can create a unique and memorable push notification sound for your app – which is something emails can never do. In some cases, push notifications can be accompanied by CTAs as well.
Also, users can receive notifications without paying a penny. That’s not the case for SMS. Some users may have to pay to receive SMS messages. If that’s so, you’re harming a user, and soon you may end up in the spam section.
Similarly, while sending bulk SMS messages, the sender number used may not directly give out hints about the app. Whereas, push notifications are accompanied by the app icon design, and so, users will have a precise idea of what they are about to tap.
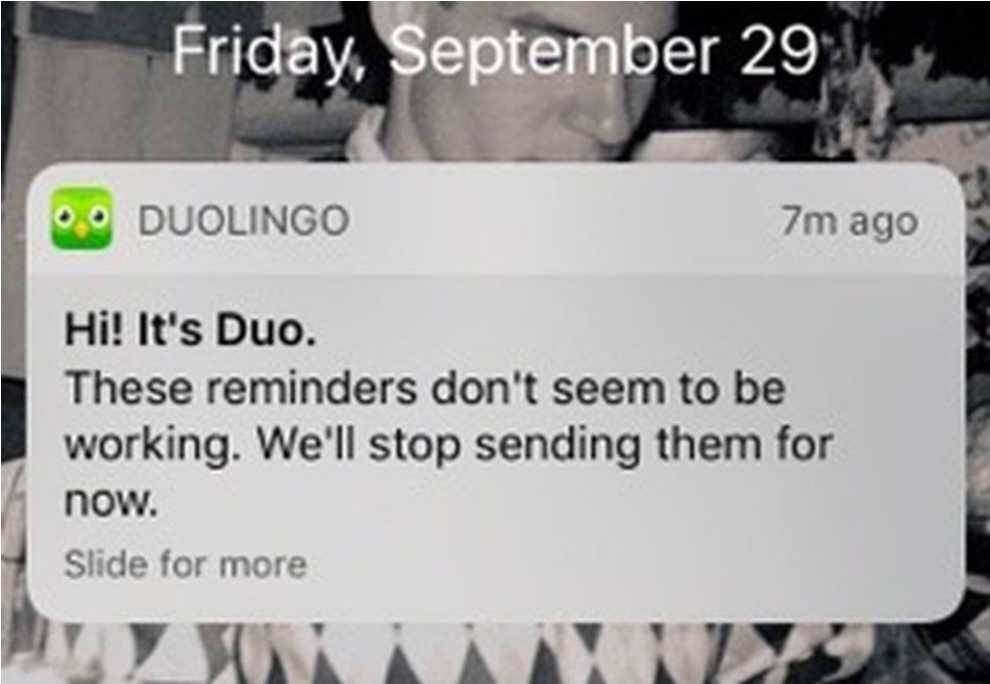 The app icon design in Duolingo’s push message. Image Credit: mashable.com
The app icon design in Duolingo’s push message. Image Credit: mashable.com
However, in terms of the character limit, emails and SMS messages win over push notifications. Push notifications can be viewed only as an alert, whereas emails and SMS messages can explain the value proposition in detail.
How Do Push Notifications Work?
Before going any deeper into how do push notifications work on Android and iOS, you need to know some critical components that make these notifications possible.
App Publisher
The entity that publishes the app in the respective app stores.
Client App
It’s the app that is installed by the users and receives the push notifications.
Operating System Push Notification Service (OSPNS)
In order to receive notifications, the mobile app must be registered and configured with an operating system push notification service (OSPNS). Each mobile operating system has its own OSPNS.
Google has Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM), whereas Apple has Apple Push Notification Service (APNS).
Push Notification Service
You will need to use a push notification service to be able to send these messages. The service lets you send notifications to the respective OSPNS, which then transmits the same to the client app. There are plenty of push notification services available today, and many help you to optimize your messaging – from content creation to the testing of your message, and its timing.
Once you’re aware of the components that make push notifications a reality, there are two other terms you need to know about – Receiver pull and Sender Push. These two are the models by which information is shared across the internet.
Receiver Pull
The receiver pull model is used when the receiver requests information.
To put that in perspective, think of what you probably do when you have a question in mind. Most likely, you head to Google Search and type in and search the query. Within milliseconds, Google will return thousands of results to choose from.
Similarly, if you’d like to watch a movie on Netflix, you type in the movie name, select from the suggestions. Then Netflix will grant you access to watch the movie.
In both cases, you (the receiver) are sending a request to a specific server whenever you need something. Once your request is met, you’ll shut down the connection until you need it again.
These kinds of information transfers in which you connect and request whenever you want something and shut down once your requests are fulfilled are based on pull protocol. The information transferred using this protocol is called a pull message or pull notification.
Hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) which is designed to communicate between web servers and browsers is a push protocol. Once you type the URL on the browser, an HTTP request is made to the web server, which then sends the requested content to your browser.
Sender Push
Unlike the previous model, the sender push model doesn’t require the receiver to request information. Instead, once the receiver allows the publisher to send information, the latter can do it anytime they want.
As you must have expected, the sender push model is based on the push protocol and the information transferred using this protocol is called a push message or push notification.
If you have been a netizen for more than a decade, then you’ll be probably aware of the RSS feed. Once you have subscribed to the RSS feed of a website, it can send you push messages whenever it wants to.
A push notification sent to users follows the same principle, but its components and tools used to send one are quite different.
Now, back to how push notifications work.
How Do Push Notifications Work on Android?
As previously mentioned, in order to receive push notifications, the app must be registered and configured with an OSPNS. Here, we’ll consider Google’s Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) – which works for both Android and iOS apps. FCM also has built-in targeting and analytics features.
 Client app registration with FCM (OSPNS). Image Credit: yalantis.com
Client app registration with FCM (OSPNS). Image Credit: yalantis.com
The OSPNS is integrated with an app with the help of a mobile SDK. Such an SDK will contain the API that will allow the app to communicate with the service. Do note that the integration process must be implemented before the app is uploaded to the app stores.
 An API key created in OSPNS, Image Credit: api-university.com
An API key created in OSPNS, Image Credit: api-university.com
Once you’ve registered with FCM, you’ll receive an API key. Also, once you’ve registered with an OSPNS (in this case, FCM), whenever a user installs your app, FCM will issue a unique registration ID for the same user’s device-app combination. This registration ID makes it possible for the app to receive notifications from an OSPNS.
The registration ID generated must be protected with the utmost confidentiality. Otherwise, it can be misused to send malicious messages.
 A simple representation of how push notifications are sent by the publisher to the user. Image Credit: twilio.com
A simple representation of how push notifications are sent by the publisher to the user. Image Credit: twilio.com
Once the device and app are registered with the FCM, the app server needs to identify the device. This identification process will allow an app server to send notifications to a user’s device on your behalf. This server identification process is performed with the help of an API key.
How Do Push Notifications Work on iOS?
The process involving Apple Push Notification Service (APNS) is different from that of FCM. Let’s take a quick look at how push notifications work in iOS with APNS.
Once a user installs an app, iOS requests a device token from APNS. Once the request is accepted, the app receives the token – which is used as the address to send push notifications. The mobile app then sends the token of the device to your app server.
When prompted, the app server will send the push notification to APNS with the device token. APNS will then send the push notification to the user’s device.
Once the system has been set up, and the client app is configured with the server and OSPNS, the app publisher can send out push notifications with ease, at any time. You can either compose manual messages with the help of a message composer or send out automated messages.
Depending on the push notification service provider you choose, you can define your target audience and send messages only to a particular group of users. You can also decide whether to send out the message immediately or at a predefined time.
The Limitations of Push Notifications
Although the push notification system is the easiest way to communicate with your users, it doesn’t always let you send out messages in the exact way you desire.
Here are some of the limitations of push notifications that may make app developers frustrated, but ultimately give more control to users.
1. The Opt-in Evil of iOS Apps
 The opt-in prompt in iOS. Image Credit: braze.com
The opt-in prompt in iOS. Image Credit: braze.com
As you probably know, the iOS operating system requires users to explicitly grant permission for an app to send them push notifications. Make sure you introduce the true value of your app as early as possible in the onboarding process to increase the opt-in rates. Fortunately, Android users are automatically opted-in to receive push notifications while installing an app.
2. The Payload Is Limited
Payload – which is the amount of text data allowed in a push notification is quite nominal. The payload limit for iOS is 2KB, whereas, for Android, it’s 4KB. On a side note, images for notifications are limited to 1MB in size in Android and 10MB in iOS.
3. The Number of Characters Is Limited
In Android, a maximum of 633 characters can be included in the push notification. Whereas for iPhones, it’s 178 characters.
4. You Can’t Be Fully Sure About the Timing
Since push messages directly hit a users notification centre, they are harder to ignore, unlike other forms of communication. Although this might seem to be an excellent opportunity for marketers, it can be not very pleasant to the users.
For example, consider a scenario in which a user is trying to make a payment and is wholly frustrated in doing so. Out of the blue, they receive your value proposition via a push message and get instantly distracted from the task. Such minor annoyances might add up and force the user to get rid of the app as a whole.
Push notifications can also be served to users at their most vulnerable moments. They might be sad, tired, or busy with work, and if the messages don’t provide any value to the user, they might question their intentions of having the app installed in the first place.
Don’t Be Too Pushy
Unlike any other forms of communication, push notifications allow app publishers to directly connect with their users. Ensure that you don’t misuse this special connection, as otherwise, users might get annoyed with your messages, turn off notifications, or in the worst-case scenario, uninstall your app.
The key is to deliver selected and critical notifications that a user will most likely find valuable. User segmentation can help a great deal with relevancy and never send messages at odd hours.
As a rule of thumb, never be too “pushy” with push notifications. If you’re sending push messages that contain offers or discounts for particular products, try using app deep links to navigate the user to specific app sections.
Related Sources to Read:
–When to Consider Mobile App Development for Your Business
–Why Mobile Apps Are Important for Your Business
–Factors to Consider When Hiring a Mobile App Development Company
–Mobile App Development Cost Estimate in Malaysia
Looking for a top-notch Mobile App Developer Malaysia? Your search ends here! Contact us now to bring your app idea to life with expert developers.
